代理
代理模式是一种设计模式,提供了对目标对象额外的访问方式,即通过代理对象访问目标对象,这样可以在不修改原目标对象的前提下,提供额外的功能操作,扩展目标对象的功能。简言之,代理模式就是设置一个中间代理来控制访问原目标对象,以达到增强原对象的功能和简化访问方式。
举个例子,我们生活中经常到火车站去买车票,但是人一多的话,就会非常拥挤,于是就有了代售点,我们能从代售点买车票了。这其中就是代理模式的体现,代售点代理了火车站对象,提供购买车票的方法。
静态代理
这种代理方式需要代理对象和目标对象实现一样的接口。
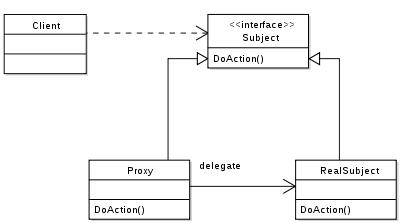
角色
Subject:被代理的接口,定义了方法DoAction();
1
2
3
4
5public interface Subject {
void doAction();
}RealSubject:原对象,真正的业务实现类,实现了Subject接口;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class RealSubject implements Subject {
public void doAction() {
System.out.println("RealSubject is doing...");
}
}Proxy:代理类,代理原对象,实现了Subject接口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16public class Proxy implements Subject {
private RealSubject subject;
public Proxy(RealSubject subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
public void doAction() {
System.out.println("Proxy is doing before");
subject.doAction();
System.out.println("Proxy is doing after");
}
}
优劣
优点
- 可以在不修改目标对象的前提下扩展目标对象的功能。
缺点
- 冗余,由于代理对象要实现与目标对象一致的接口,会产生过多的代理类;
- 不易维护,一旦接口增加方法,目标对象与代理对象都要进行修改。
动态代理
动态代理是在实现阶段不用关心代理谁,而在运行阶段才动态的指定代理哪一个对象。
jdk
jdk中使用到了一个接口InvocationHandler和一个代理类Proxy ,这两个类配合使用实现了动态代理的功能。InvocationHandler 并实现它的invoke方法,然后再用Proxy的工厂方法newProxyInstance()创建一个代理对象,这个对象同样可以实现对具体类的代理功能。而且想代理哪个具体类,只要给Handler(以下代码中的Invoker)的构造器传入这个具体对象的实例就可以了。
示例
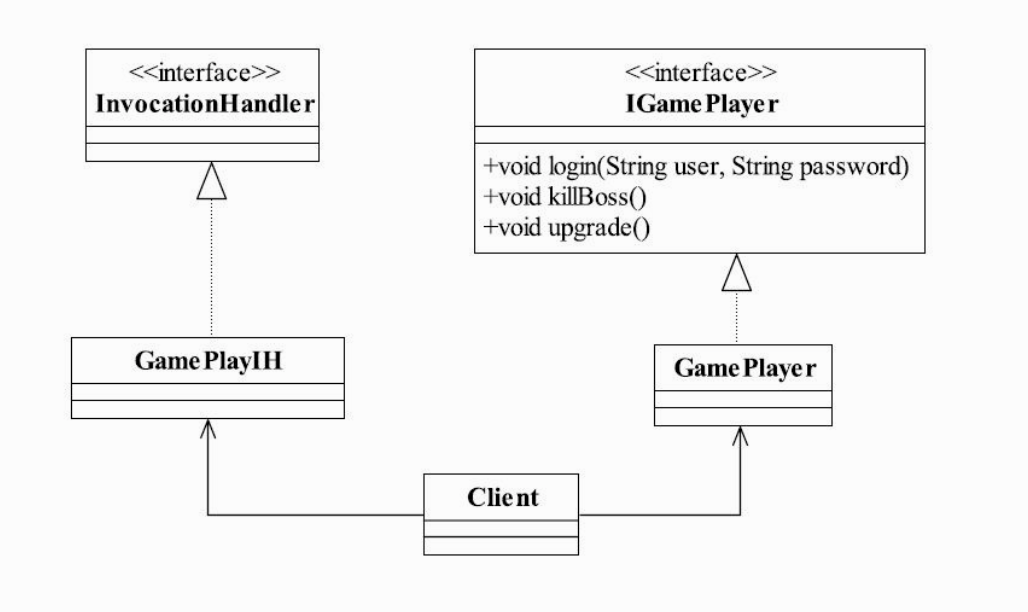
1 | public interface IGamePlayer { |
1 | public class GamePlayer implements IGamePlayer { |
1 | public class GamePlayerIH implements InvocationHandler { |
1 | public class DynamicProxy { |
原理
InvocationHandler接口
InvocationHandler接口只定义了一个invoke()方法。通过InvocationHandler接口,所有方法都由该Handler来进行处理,即所有被代理的方法都由InvocationHandler接管实际的处理任务。
1 | public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) |
- proxy:代理类对象;
- method:代理类调用的具体方法;
- args:方法的参数。
Proxy类
Proxy类提供创建动态代理类和实例的static方法,并且通过这些方法创建所有动态代理类的父类。
1 | public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, |
cglib
cglib是一个强大的、高性能的代码生成库。它被广泛使用在基于代理的AOP框架提供方法拦截。在实现内部,CGLIB库使用了ASM这一个轻量但高性能的字节码操作框架来转化字节码,产生新类。
AOP
TODO